-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Viswanadham Sridhara, Aron Marchler-Bauer, Stephen H. Bryant, Lewis Y. Geer, Automatic annotation of experimentally derived, evolutionarily conserved post-translational modifications onto multiple genomes, Database, Volume 2011, 2011, bar019, https://doi.org/10.1093/database/bar019
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
New generation sequencing technologies have resulted in significant increases in the number of complete genomes. Functional characterization of these genomes, such as by high-throughput proteomics, is an important but challenging task due to the difficulty of scaling up existing experimental techniques. By use of comparative genomics techniques, experimental results can be transferred from one genome to another, while at the same time minimizing errors by requiring discovery in multiple genomes. In this study, protein phosphorylation, an essential component of many cellular processes, is studied using data from large-scale proteomics analyses of the phosphoproteome. Phosphorylation sites from Homo sapiens, Mus musculus and Drosophila melanogaster phosphopeptide data sets were mapped onto conserved domains in NCBI’s manually curated portion of Conserved Domain Database (CDD). In this subset, 25 phosphorylation sites are found to be evolutionarily conserved between the three species studied. Transfer of phosphorylation annotation of these conserved sites onto sequences sharing the same conserved domains yield 3253 phosphosite annotations for proteins from coelomata, the taxonomic division that spans H. sapiens, M. musculus and D. melanogaster. The method scales automatically, so as the amount of experimental phosphoproteomics data increases, more conserved phosphorylation sites may be revealed.
Introduction
Protein phosphorylation is a covalent post-translational modification, which plays an important role in many cellular processes. Many eukaryotic proteins can be phosphorylated in essential cellular processes, such as signaling. Low-throughput biochemical experiments have been used to identify phosphorylation sites for decades, but the number of identified phosphosites found via in vivo labeling, 2D gel electrophoresis, antiphosphoamino acid antibodies and other methods is low compared to those found by high-throughput methods like mass spectrometry-based proteomics. In the last few years, these tandem mass spectrometry methods (1) have been used in the large-scale identification of phosphorylation sites, although the error rate of these experiments is difficult to estimate (2). These techniques utilize separation technologies such as IMAC or TiO2 chromatography and gas phase ion chemistry such as electron transfer dissociation (ETD), electron capture dissociation (ECD) and/or collision-induced dissociation (CID) that allow analysis of thousands of phosphopeptides in a single experiment (3–10). MS/MS sequence search algorithms (11–19) are used to match the peptide sequence from the tandem mass spectrometry data and to identify the phosphorylation sites. While some algorithms assign a probability to the identification of a phosphopeptide, others use site localization algorithms (20–22) to assign confidence.
Increasingly, the proteomics data from these studies is stored in various public repositories, such as NCBI Peptidome (23), Global Proteome Machine Database (24), Tranche (25), PRIDE (26), Human Proteinpedia (27) and Peptide Atlas (28). The availability of this data has helped spur several studies in evolutionary biology of phosphorylation (29, 30). The eukaryotic study by Boekhorst et al. (29) compared the phosphoproteome of six different species, and concluded that the conservation of phosphorylation sites between species is higher than expected by chance, indicating functional relevance. Until recently, there was sparse evidence for S/T/Y phosphorylation in bacteria. Prokaryotic studies examined S/T/Y phosphorylation in bacterial phosphoproteomes in Bacillus subtilis (31) and Escherichia coli (32). Before the study on B. subtilis, evidence for only 16 phosphorylation sites in 8 proteins had been gathered for this model Gram-positive bacterium. The study identified 103 phosphorylation sites in 78 B. subtilis proteins, and was the first large-scale phosphoproteomics study in bacteria (31). The same group followed up with a study on E. coli and identified 105 phosphorylation sites in 79 E. coli proteins (32). A comparison of the two bacterial phosphoproteomes revealed similarities in phosphorylation distribution, the classes of proteins involved in phosphorylation and 14 orthologous proteins, many of which were involved in glycolysis (32). From these preliminary studies on a limited set of bacteria, the authors also concluded that the phosphorylated sites are conserved more than their un-modified counterparts (32).
One issue with these high-throughput proteomics studies is lack of verification of the phosphorylation site within the phosphorylated peptide. For example, it has been shown that phosphate group can rearrange during the process of collision induced dissociation (CID), increasing the ambiguity in identifying phosphorylation sites (33). Moreover, if the peptide sequence has multiple sites that could be phosphorylated, identifying the precise location of a match can be computationally ambiguous. We propose a method to verify evolutionarily conserved phosphorylation sites by using high-throughput data: the correct identification of a phosphorylation site is more likely if there is evidence for the site in different data set or proteins from other species that are closely related in molecular evolution and have conserved function. Finding functionally similar sequences in evolutionarily related species requires algorithms to accurately align protein sequences and examine regions of conservation. For our analysis, we used domain models in a manually curated subset of NCBI’s Conserved Domain Database (CDD).
Proteins often share domains that are evolutionarily conserved units of function and 3D structure. In general, smaller proteins have 1- or 2-domains, while larger proteins may have more than two domains. Detailed descriptions of protein domain families and their evolution can be found elsewhere (34). These domains are identified and classified into protein families by comparative analysis techniques, such as structure sequence alignment followed by the creation of phylogenetic trees. This classification and annotation can include conserved functional sites assigned by curators, including some of the phosphorylation sites examined in this article.
There are numerous protein family databases available that store protein domains along with the entire protein sequences such as Pfam (35), SMART (36), COG (37), CDD (38). In general, these databases are a collection of annotated multiple sequence alignments, which represent the evolutionarily conserved domains. These domain models can be rapidly and automatically applied to genomes using algorithms such as RPS-BLAST (39) and HMMER (40). In our analysis, we rely on domain models from NCBI’s Conserved Domain Database that are curated by NCBI and on the RPS-BLAST algorithm. One advantage of using NCBI curated domain models is that they often classify protein domains into functionally specific sub-families which may not be the case with other domain databases that focus on overall coverage, such as Pfam. Even within a single organism, a particular domain family may have quite different functions, although they tend to be related biochemically. Each CDD sub-family is meant to capture a specific function that has been conserved for several hundred million years. A site may rapidly evolve within a particular domain family and, if so, it would be incorrect to transfer the annotation of such a site to all sequences within that family. In particular, phosphorylation sites have been shown to evolve rapidly (30), implying that very fine-grained sub-family assignment within protein families may be required for the proper transfer of such annotation onto related genomes.
An additional advantage of the NCBI curated models is that they include functional sites only if there is evidence for the site in the literature, or if the sites can be inferred from 3D structures. If a functional site is restricted to a sub-family, it is only mapped onto protein sequences that have high scoring (specific) hits to that sub-family. Applying such a set of rules, it becomes possible to annotate sites onto multiple genomes without generating a large number of false assignments. However, the manual curation of these functionally relevant sites is laborious, requiring extensive literature searches, analysis of available 3D structure and expert judgment by curators. With data obtained from high-throughput proteomics experiments, automatic site identification may enhance and significantly speed-up the curation process. Coupled with the automatic mapping of sites via profile search methods such as RPS-BLAST or HMMER, PTM sites can be computationally annotated onto other genomes in a matter of minutes. This ability is especially important as genome sequencing becomes more affordable (41) and the number of sequenced genomes increases at a higher rate.
A variety of well-established methods are available for the prediction of phosphorylation sites (42). Common approaches (43–45) are based on the detection of short characteristic protein sequence motifs (46). Most protein kinases achieve specificity for their protein targets by recognizing sites that are more extensive than the single residue that is to be modified (47). A collection of such motif sequences is extremely useful in predicting the location of phosphorylation sites in particular sequences of interest. However, the limited size of the motifs and their degeneracy will generate many false positives if applied to a large number of protein sequences. Other, more generalized methods rely on machine learning methods and statistical profiles (48, 49) trained on in vivo and in vitro experimental data. They attempt to capture information on conservation and interresidue relationships in the phosphorylation sites, but typically do not consider family classifications based on phylogenetic analyses. Considering such phylogenetic evidence, one would expect to observe phosphorylation at a particular site with greater likelihood, if phosphorylation has been observed at the matching site in a closely related protein. This type of phylogenetic analysis may help avoid misclassification and may provide a method for applying the classifier to genomes in the same narrow phylogenetic branches. Additionally, the machine learning methods do not address the issue of false positives in the training set, as there is wide variance in the reported error rates in high-throughput proteomics experiments. HAMAP (50) is an annotation system that uses manually curated family rules (motifs, taxonomic coverage etc.) to determine which functional site annotations could be potentially propagated onto other sequences within well-defined families and sub-families. In the method outlined here, we aim to automatically restrict the analysis to evolutionarily conserved sites and then automatically apply the filtered experimental data to manually curated functional sub-families, which allows us to annotate phosphorylation sites within other related genomes with high confidence without resorting to manual curation of the individual phosphorylation sites.
Results
Determining the evolutionary conservation of phosphorylation sites requires mapping the experimental data onto protein sequences that are stably mapped onto genomes. The sequences must then be aligned into evolutionarily conserved groups to compare the sites across species.
Proteins and their conserved domains
Homo sapiens, Mus musculus and Drosophila melanogaster protein sequences were downloaded from RefSeq (51). RefSeq is intended to be a comprehensive and non-redundant set of protein sequences that provides a stable reference for genome annotation. There were 39 172 human, 36 422 mouse and 21 779 fruit fly sequences. Each sequence was identified by an integer number, the GI.
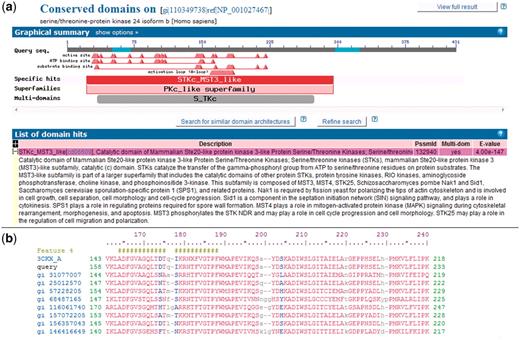
To compare sequences across genomes, we used the domain models in the NCBI CDD database (version 2.22). These domains are identified by PSSM-ID (Position-Specific Scoring Matrix ID). There are two levels of stringency used to label the protein domain assignments in NCBI CDD (38), given the protein sequence. RPS-BLAST identifies footprints of protein domains present within the protein sequence. The top scoring assignment (domain model) for a particular query region is again evaluated to see if the score is above a pre-computed domain specific score threshold. These high-confidence assignments, also called specific hits, imply that the query protein sequence belongs to the same protein family as the sequences used to create the domain model and provide the most accurate inference of function. If no specific hit can be assigned, RPS-BLAST defaults to indicate membership in a domain super-family. RPS-BLAST search results for a query protein sequence are shown in Figure 1.
NCBI Conserved Domains annotated on a protein query. (a) RPS-BLAST is used to find domain footprints and derived functional sites using a serine–threonine protein kinase as a protein query (GI 110349738). Shown in red is a specific hit, i.e. a protein sub-family identified with high confidence. (b) Example of a multiple sequence alignment (MSA) representing a CDD domain. The alignable regions (structured blocks or block alignments) are shown in upper case blocks, while the unaligned regions are shown as lower case and gaps. NCBI CDD also can provide functional site annotation. The hash marks indicate the annotation of an activation loop (A-loop). The row starting with ‘query’ shows the protein query (GI:110349738) with start and stop sites.
The first step in our analysis is identifying specific hits within each proteome in the three organisms studied here. Given the GI sequence identifiers, the PSSM ID(s) that correspond to specific hits of domains to the sequences are identified. This information was retrieved from the CDART database (52), which stores pre-calculated RPS-BLAST hits of conserved domains on proteins. There are 12 929 human GI’s which have at least one domain assignment that is identified as ‘specific hit’. Similarly, there are 11 603 and 7587 mouse and fly GI’s which map to at least one ‘specific hit’. These sequence records in human, mouse and fly map to 2495, 2376 and 1632 unique ‘specific hits’, respectively. The number of ‘specific hits’ that are common to all three organisms is 1469.
Evolutionary conservation of phosphosites
Experimental human phosphosite data were obtained from supplementary information provided by Tan et al. (30). The authors obtained and processed the human phosphopeptide data sets from two online databases Phospho.ELM (53) and PhosphoSite (54), which stores phosphosites obtained from low throughput (LTP), high throughput (HTP) and cell signaling technology (CST). In total, there are 23 977 unique human phosphorylation sites from 6456 proteins with ENSEMBL ids. The fruit fly phosphopeptide set was obtained from mass spectrometry-based proteomics data provided by the Gygi lab (8), the results of large-scale identification of phosphopeptides from Drosophila embryos. Sequest (14) was used to identify phosphopeptides from MS/MS spectra and subsequently Ascore (21) was used to assign confidence to the phosphosite localization within the phosphopeptides. From this LC–MS/MS analysis on D. melanogaster, 13 720 unique phosphorylation sites were identified in 2702 proteins with FlyBase ids. Mouse phosphosite data sets were obtained from two different sources (6, 7) with 5635 sites matched to 2328 IPI proteins and 5433 sites matched to 1808 IPI proteins. When Ascore was used in one of the mouse data sets (7) and the fly phosphopeptide set, we required 95% site localization certainty. In the other mouse data set (6), MaxQuant (55) was used to assign phosphorylation site after sequence search with Mascot (15). All of the phosphopeptide data were then mapped onto RefSeq sequence records with matching taxonomic identifier to obtain GI’s and start and stop positions.
Given GIs and phosphosite positions, we identify corresponding positions on the domain model alignments that map to the experimentally identified phophorylation sites via specific hits. A domain model consists of aligned blocks and unaligned regions between those blocks, as shown in Figure 1b. Since the unaligned regions within the domain models cannot be reliably aligned with each other, we only examined the distribution of phosphosites mapped to the structured alignment blocks.
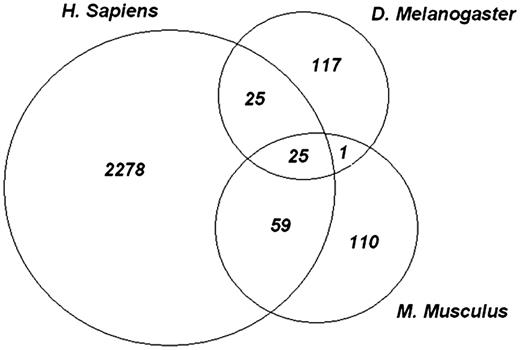
In the human proteome, 2378 phosphorylation sites can be mapped onto structured blocks within 853 specific domain hits. One hundred and sixty-nine fruit fly phosphorylation sites can be mapped to structured blocks within 99 specific domain hits and 196 mouse phosphorylation sites can be mapped to structured blocks within 119 specific domain hits. Out of these specific hits, there were 29 PSSM-IDs which were found in all three organisms. Requiring positional conservation of the phosphorylation sites yielded 26 unique phosphorylation sites, which were mapped to 19 common domain models (same PSSM-ID) across all 3 organisms. Of these 26 sites, 1 site was found in the RRM domain, which has no detailed sub-family hierarchy in CDD at this time. Figure 2 shows the number of conserved phosphosites between human, mouse and fly as mapped to structured alignment blocks.
Evolutionarily conserved phosphosites. Each of the experimental phosphopeptide data sets were mapped onto conserved domain-specific hits and the site positions on the domain models were examined for overlap. The Venn diagram shows the number of sites that overlap between each species and among all three species. Twenty five highly conserved phosphorylation sites are shared by all species.
The number of conserved phosphosites identified this way could be small for at least two reasons: (i) First, the number of phosphosites from fly and mouse data sets that are found in specific hits is small because of incomplete data sets, (ii) second, the overall number of specific domain assignments shared by 3 genomes under study is 1469, which is a small fraction of the total number of proteins and their constituent domains in each genome. However, over time the amount of experimental data from these species and the number of specific assignments available through curation of the domain database should increase considerably.
The rationale for requiring three separate identifications of a conserved phosphorylation site was based on the fact that there is some ambiguity in phosphorylation sites identified from high-throughput phosphoproteomics data (56). This site localization ambiguity could be from experimental issues, such as labile post-translational modifications, or from computational methods, such as an inability to specifically assign a phosphorylation site within a phosphorylated peptide. Phosphosite evidence from more than one organism should help reduce the false positives. To understand this effect, we examined 50 sites that are conserved in human and fly. Of these, 20 sites were already annotated in CDD. There is also evidence for 12 more sites in published literature. This leaves out 18 sites, of which 3 sites were annotated on sequence records as being observed in large-scale phosphoproteomics experiments based on mass spectrometry, similar to the data used in the current study. There is no evidence of phosphorylation on sequence records for the remaining 15 sites (∼30% of total sites). It seems possible that some of these could be novel conserved sites and that evidence from another organism would confirm them. When we required 3 species to confirm a phosphorylation site, 25 sites were identified. Out of these sites, 12 were already annotated in CDD. Of the remaining 13 sites, there was supporting experimental evidence from the literature for 12 sites, while the site identified in the ribosomal protein L11 had no evidence from low-throughput experiments, but annotated as being identified using high-throughput methods.
Large-scale automatic annotation of phosphosites
Currently, approaches to validating identified phosphopeptides range from manual curation (3) to automatic curation using site localization algorithms (8–10). Here, we propose that the identification of a phosphosite in an evolutionarily conserved location, as observed in three different organisms, provides strong evidence for a conserved, biologically significant phosphorylation site. Considering the strength of this evidence, it may seem reasonable to transfer the conserved site annotation to corresponding evolutionarily conserved locations across the entire clade which spans these organisms.
Using sites that appear conserved between human, mouse and fruit fly, we have attempted large-scale automatic annotation on multiple genomes in coelomata, which is the common taxonomy node covering the three species. Currently, this clade contains 910 530 unique protein sequences from the RefSeq database, spanning a total of 1869 different organisms. The annotation procedure resulted in 18 818 annotated phosphorylation sites in 12 068 sequence records from 53 different species. In eukaryotes, protein phosphorylation is generally observed on serine(S), threonine(T) or tyrosine(Y) side chains. Mapping phosphorylation sites onto amino acids that are not amenable to phosphorylation is meaningless, of course, and restricting the sites to contain either serine, threonine, or tyrosine resulted in 11 755 phosphorylation sites in 9088 sequence records from 53 different organisms. There are several possible reasons for the difference between the total number of putative phosphorylation sites that can be annotated by mapping across alignments, and the number of resulting sites that are actually amenable to phosphorylation. A small subset of the protein domain families in CDD have not been fully characterized at the sub-family hierarchy level, resulting in overly generic ‘specific hits’ and inviting incorrect mapping of phosphorylation sites onto a subset of sequence records covered by the corresponding protein domain family. One such family is the RNA Recognition Motif (RRM), that contains one of the conserved sites identified in this analysis. Transferring this site annotation onto sequences in coelomata resulted in a total of 15 162 putative sites, and restricting the sites to be a S/T/Y resulted in 8502 sites (56%). This relatively low rate of annotation may indicate that some sub-families of RRM do not contain this phosphorylation site and serves as an example of why the detailed sub-family hierarchy in CDD can be useful in defining protein function. Excluding the RRM site from the analysis results in 3253 sites that contain S/T/Y out of a possible 3656 sites, indicating that 89% of sites are amenable to phosphorylation. This higher rate of annotation highlights the importance of maintaining evolutionary and functional sub-families in domain classifications, as some sub-families may have diverse biological functions that do not have or require the phosphosite (57). Because of this, we restricted our analysis only to functional sub-families.
Another reason for putative phosphorylation sites being mapped to incompatible residue types is that automatic transfer of the modification annotation onto other sequence records depends on the accuracy of the multiple alignment models that define the domains. To estimate the effect of alignment ambiguity, we analyzed the sites remaining after exclusion of the RRM. Even though the number of sites that are not phosphorylatable is small (403 in total), we examined the effect of misalignment or site ambiguity in the multiple sequence alignment of the protein family. To do this, we examined amino acids around the site of interest on the annotated sequence and looked for a possible phosphorylation site within offsets of ±1 to ±3 alignment positions relative to the site. As the offset increases the number of additional sites that are amenable to phosphorylation dropped. For example, an offset of ±1AA resulted in 119 sites that can be phosphorylated, while for ±2AA, it is 22 sites and for ± 3AA, there is only 1 site that is amenable to phosphorylation. Considering sites which are off by ±1AA to ±2AA contributes to only 3% of the total number of phosphosites suggesting that the alignments within CDD are positionally specific. Thus, the total number of evolutionarily conserved sites that were mapped to functional sub-families is 25, excluding the RRM domain, which does not have a detailed sub-family hierarchy in CDD at this time. Table 1 lists the PSSM-ID’s and the names of the domain models in NCBI CDD database that have conserved sites.
List of protein families with conserved phosphosites
| PSSM-ID . | Sites . | Protein family (NCBI CDD) and description . |
|---|---|---|
| 28 957 | 32b | H4:Histone H4. |
| 30 346 | 33b | AMPKbeta_GBD_like:AMP-activated protein kinase beta subunit glycogen binding domain. |
| 48 161 | 43b | GroEL:GroEL_like type I chaperonin. |
| 48 163 | 234b; 236a; 241a | TPP_E1_PDC_ADC_BCADC:Thiamine pyrophosphate family. |
| 100 088 | 44b | PGM3: phosphoglucomutase 3. |
| 100 101 | 26c | Ribosomal_L11:Ribosomal protein L11. |
| 107 222 | 107b | p23_hB-ind1_like:p23_like domain found in human (h) butyrate-induced transcript 1 (B-ind1) and similar proteins. |
| 132 804 | 45b | PX_SNX3_like:The phosphoinositide binding Phox Homology domain of Sorting Nexin 3 and related proteins. |
| 132 940 | 157a | STKc_MST3_like:Catalytic domain of Mammalian Ste20-like protein kinase 3-like Protein Serine/Threonine Kinases. |
| 132 979 | 174a | STKc_PAK_II:Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, Group II p21-activated kinase. |
| 143 346 | 154a; 160a | STKc_CDK7:Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase 7. |
| 143 354 | 167a; 169a | STKc_ERK1_2_like:Catalytic domain of Extracellular signal-Regulated Kinase 1 and 2-like Serine/Threonine Kinases. |
| 143 356 | 173a; 175a | STKc_p38:Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase. |
| 173 660 | 152b | STKc_AGC:Catalytic domain of AGC family Protein Serine/Threonine Kinases. |
| 173 673 | 295b; 299a | STKc_RSK_N:N-terminal catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, 90 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase. |
| 173 680 | 302a | STKc_PKN:Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, Protein Kinase N. |
| 173 752 | 12b; 13b | STKc_CDK1_euk:Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase 1. |
| 176 301 | 50b | PH_Cool_PixCool Pix pleckstrin homology (PH) domain. |
| PSSM-ID . | Sites . | Protein family (NCBI CDD) and description . |
|---|---|---|
| 28 957 | 32b | H4:Histone H4. |
| 30 346 | 33b | AMPKbeta_GBD_like:AMP-activated protein kinase beta subunit glycogen binding domain. |
| 48 161 | 43b | GroEL:GroEL_like type I chaperonin. |
| 48 163 | 234b; 236a; 241a | TPP_E1_PDC_ADC_BCADC:Thiamine pyrophosphate family. |
| 100 088 | 44b | PGM3: phosphoglucomutase 3. |
| 100 101 | 26c | Ribosomal_L11:Ribosomal protein L11. |
| 107 222 | 107b | p23_hB-ind1_like:p23_like domain found in human (h) butyrate-induced transcript 1 (B-ind1) and similar proteins. |
| 132 804 | 45b | PX_SNX3_like:The phosphoinositide binding Phox Homology domain of Sorting Nexin 3 and related proteins. |
| 132 940 | 157a | STKc_MST3_like:Catalytic domain of Mammalian Ste20-like protein kinase 3-like Protein Serine/Threonine Kinases. |
| 132 979 | 174a | STKc_PAK_II:Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, Group II p21-activated kinase. |
| 143 346 | 154a; 160a | STKc_CDK7:Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase 7. |
| 143 354 | 167a; 169a | STKc_ERK1_2_like:Catalytic domain of Extracellular signal-Regulated Kinase 1 and 2-like Serine/Threonine Kinases. |
| 143 356 | 173a; 175a | STKc_p38:Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase. |
| 173 660 | 152b | STKc_AGC:Catalytic domain of AGC family Protein Serine/Threonine Kinases. |
| 173 673 | 295b; 299a | STKc_RSK_N:N-terminal catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, 90 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase. |
| 173 680 | 302a | STKc_PKN:Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, Protein Kinase N. |
| 173 752 | 12b; 13b | STKc_CDK1_euk:Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase 1. |
| 176 301 | 50b | PH_Cool_PixCool Pix pleckstrin homology (PH) domain. |
aCDD phosphorylation annotation.
bLiterature (LTP)
cNo evidence.
List of protein families with conserved phosphosites
| PSSM-ID . | Sites . | Protein family (NCBI CDD) and description . |
|---|---|---|
| 28 957 | 32b | H4:Histone H4. |
| 30 346 | 33b | AMPKbeta_GBD_like:AMP-activated protein kinase beta subunit glycogen binding domain. |
| 48 161 | 43b | GroEL:GroEL_like type I chaperonin. |
| 48 163 | 234b; 236a; 241a | TPP_E1_PDC_ADC_BCADC:Thiamine pyrophosphate family. |
| 100 088 | 44b | PGM3: phosphoglucomutase 3. |
| 100 101 | 26c | Ribosomal_L11:Ribosomal protein L11. |
| 107 222 | 107b | p23_hB-ind1_like:p23_like domain found in human (h) butyrate-induced transcript 1 (B-ind1) and similar proteins. |
| 132 804 | 45b | PX_SNX3_like:The phosphoinositide binding Phox Homology domain of Sorting Nexin 3 and related proteins. |
| 132 940 | 157a | STKc_MST3_like:Catalytic domain of Mammalian Ste20-like protein kinase 3-like Protein Serine/Threonine Kinases. |
| 132 979 | 174a | STKc_PAK_II:Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, Group II p21-activated kinase. |
| 143 346 | 154a; 160a | STKc_CDK7:Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase 7. |
| 143 354 | 167a; 169a | STKc_ERK1_2_like:Catalytic domain of Extracellular signal-Regulated Kinase 1 and 2-like Serine/Threonine Kinases. |
| 143 356 | 173a; 175a | STKc_p38:Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase. |
| 173 660 | 152b | STKc_AGC:Catalytic domain of AGC family Protein Serine/Threonine Kinases. |
| 173 673 | 295b; 299a | STKc_RSK_N:N-terminal catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, 90 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase. |
| 173 680 | 302a | STKc_PKN:Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, Protein Kinase N. |
| 173 752 | 12b; 13b | STKc_CDK1_euk:Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase 1. |
| 176 301 | 50b | PH_Cool_PixCool Pix pleckstrin homology (PH) domain. |
| PSSM-ID . | Sites . | Protein family (NCBI CDD) and description . |
|---|---|---|
| 28 957 | 32b | H4:Histone H4. |
| 30 346 | 33b | AMPKbeta_GBD_like:AMP-activated protein kinase beta subunit glycogen binding domain. |
| 48 161 | 43b | GroEL:GroEL_like type I chaperonin. |
| 48 163 | 234b; 236a; 241a | TPP_E1_PDC_ADC_BCADC:Thiamine pyrophosphate family. |
| 100 088 | 44b | PGM3: phosphoglucomutase 3. |
| 100 101 | 26c | Ribosomal_L11:Ribosomal protein L11. |
| 107 222 | 107b | p23_hB-ind1_like:p23_like domain found in human (h) butyrate-induced transcript 1 (B-ind1) and similar proteins. |
| 132 804 | 45b | PX_SNX3_like:The phosphoinositide binding Phox Homology domain of Sorting Nexin 3 and related proteins. |
| 132 940 | 157a | STKc_MST3_like:Catalytic domain of Mammalian Ste20-like protein kinase 3-like Protein Serine/Threonine Kinases. |
| 132 979 | 174a | STKc_PAK_II:Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, Group II p21-activated kinase. |
| 143 346 | 154a; 160a | STKc_CDK7:Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase 7. |
| 143 354 | 167a; 169a | STKc_ERK1_2_like:Catalytic domain of Extracellular signal-Regulated Kinase 1 and 2-like Serine/Threonine Kinases. |
| 143 356 | 173a; 175a | STKc_p38:Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase. |
| 173 660 | 152b | STKc_AGC:Catalytic domain of AGC family Protein Serine/Threonine Kinases. |
| 173 673 | 295b; 299a | STKc_RSK_N:N-terminal catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, 90 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase. |
| 173 680 | 302a | STKc_PKN:Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, Protein Kinase N. |
| 173 752 | 12b; 13b | STKc_CDK1_euk:Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase 1. |
| 176 301 | 50b | PH_Cool_PixCool Pix pleckstrin homology (PH) domain. |
aCDD phosphorylation annotation.
bLiterature (LTP)
cNo evidence.
An example of the biological importance of evolutionarily conserved phosphorylation sites
One of the conserved phosphorylation sites identified in the above analysis is Ser 47 in histone H4. PTM’s on histone proteins play important roles in the activation and inactivation of chromatin, by creating changes in structure and function. H4 is a highly conserved histone and contacts many other histones in the nucleosome complex. The H4 Ser 47 site is annotated as a DNA-binding site on sequence records, but not as phosphorylation site (58). A literature survey on this phosphorylation site uncovered several publications on the search for the corresponding protein kinase (58–60). The phosphorylation site might play a role in histone–histone interaction and in chromatin assembly, but has not been investigated in great detail (59). Examining this protein family in CDD, Ser 47 is shown to be highly conserved from human to yeast, i.e. invariant across ∼2 billion years of evolution. In contrast, Ser 1 on histone H4 is annotated as phosphorylated in many sequence records, and has been studied in depth (61–63). Ser 1 is involved in nuclear compaction during sporulation in budding yeast (61). These studies also show that SPS1, a serine/threonine kinase is required for phosphorylation of Ser1 on H4 during sporulation (63). Ser1 phosphorylation is also seen during spermatogenesis in D. melanogaster and in mouse cells, showing evolutionary conservation of this site (62). While the reproductive function of Ser1 phosphorylation is not exactly the same across a significant period of evolution, it is clear that Ser1 plays significant part in the function of histone H4. Similarly, the comparable evolutionary conservation of Ser 47 phosphorylation suggests that it also has a significant part to play in the function of H4, and may well be a target worthwhile of in-depth biochemical studies.
Methods
Scripts and programs used for our computational analyses were written in c++, Matlab and SPlus.
Theory—domains and their distribution
At the time of analysis, RefSeq (release 41) included almost 10 million protein sequences in 10 567 organisms. To identify the ‘specific hits’ within these proteins, the CDART database is used (52). To understand the protein–domain mapping within proteomes, we identified all sequence records that map to at least one ‘specific hit’ using RPS-BLAST and the algorithm described by Fong et al. (64). We also identified the number of ‘specific hits’ that were common to all three species.
Evolutionary conservation of phosphosites
Outlined below are the steps used to map phosphopeptides onto protein sequences in RefSeq, and then onto the protein domain (if any), including the position of the phosphorlyation site on the domain model.
Identify the protein
Given the phosphopeptide sequence and the position of the phosphosite(s), we identified the corresponding RefSeq sequence record along with the site(s) using string matching of the peptide sequence to the protein sequence.
Identify the specific domain hit
Given the sequence record, ‘specific hits’ are identified, if any. The CDART database stores all the domain model hits to the sequences that have an E-value at or below 0.01.
Map the phosphorylation site
Given the phosphorylation position on sequence record, the position of the phosphorylation site with respect to the ‘specific hit’ domain model can be calculated using the RPS-BLAST alignments found in the NCBI CDART database.
Identify conserved site
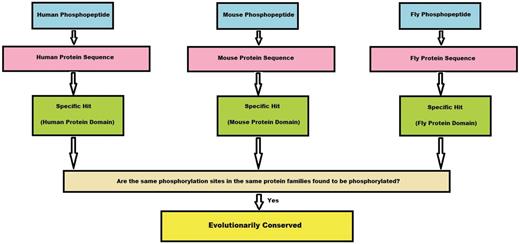
If a protein family has a phosphorylation site mapped from all the three species (human, mouse and fly), we count this site as conserved. This algorithm is given as a flowchart in Figure 3.
Algorithm flowchart. This flowchart explains in brief how a conserved site is obtained from the experimental phosphopeptide data sets from three species. First, a phosphopeptide is mapped to its protein sequence and later onto specific hits, if any. If the phosphosites from these three species map to the same position on the specific hit, we consider the site to be conserved.
Automatic functional site annotation
We transferred the annotation of conserved phosphorylation sites onto evolutionarily related sequences. In the NCBI taxonomy database, coelomata is the common taxonomy node that spans human, mouse and fly. All protein sequences in coelomata clade were downloaded. Using RPS-BLAST and CDD domain definitions, conserved phosphosites as determined earlier were mapped from the domain models onto applicable sequences in this clade. Iterating through all the protein sequence records (GI’s), we stored the sequences along with the phosphorylation positions which map the conserved sites on specific hits. These results are available at ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/lewisg/data/sridhara10/.
Conclusions
This article proposes a novel method to automatically use experimentally derived phosphorylation data to identify evolutionarily conserved phosphorylation sites within conserved domains, and to extend these annotations onto related genomes. This is an increasingly important task due to innovations in next generation sequencing and is achieved by: (i) mapping phosphosites onto conserved domains by using phosphosite data sets from human, mouse and fruit fly; (ii) finding phosphosites that are conserved between these three species; and (iii) transferring annotation of these evolutionarily conserved phosphosites onto other evolutionarily related protein sequences. We found 3253 sites that can be annotated on protein sequences assigned to the clade of coelomata, which is the common taxonomy node of human, mouse and fly.
Over time, increases in the number of domains annotated on sequence records and in the number of phosphoproteomics studies are expected to also increase the number of evolutionarily conserved sites that can be detected by the proposed method. Moreover, novel evolutionarily conserved phosphorylation sites could emerge from such analysis and the method could be extended to other post-translational modifications.
Funding
Intramural Research Program of the NIH, National Library of Medicine. Funding included open access charge.
Conflict of interest. None declared.
Acknowledgements
We thank Naigong Zhang for providing the data mapping conserved domains onto proteins. We also thank the Information Engineering Branch of NCBI for much of the software used in the paper.