-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Dan Shao, Lan Huang, Yan Wang, Xueteng Cui, Yufei Li, Yao Wang, Qin Ma, Wei Du, Juan Cui, HBFP: a new repository for human body fluid proteome, Database, Volume 2021, 2021, baab065, https://doi.org/10.1093/database/baab065
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
Body fluid proteome has been intensively studied as a primary source for disease biomarker discovery. Using advanced proteomics technologies, early research success has resulted in increasingly accumulated proteins detected in different body fluids, among which many are promising biomarkers. However, despite a handful of small-scale and specific data resources, current research is clearly lacking effort compiling published body fluid proteins into a centralized and sustainable repository that can provide users with systematic analytic tools. In this study, we developed a new database of human body fluid proteome (HBFP) that focuses on experimentally validated proteome in 17 types of human body fluids. The current database archives 11 827 unique proteins reported by 164 scientific publications, with a maximal false discovery rate of 0.01 on both the peptide and protein levels since 2001, and enables users to query, analyze and download protein entries with respect to each body fluid. Three unique features of this new system include the following: (i) the protein annotation page includes detailed abundance information based on relative qualitative measures of peptides reported in the original references, (ii) a new score is calculated on each reported protein to indicate the discovery confidence and (iii) HBFP catalogs 7354 proteins with at least two non-nested uniquely mapping peptides of nine amino acids according to the Human Proteome Project Data Interpretation Guidelines, while the remaining 4473 proteins have more than two unique peptides without given sequence information. As an important resource for human protein secretome, we anticipate that this new HBFP database can be a powerful tool that facilitates research in clinical proteomics and biomarker discovery.
Database URL: https://bmbl.bmi.osumc.edu/HBFP/
Background
Human body fluids are thought to be rich resources of disease-associated proteins that are secreted or leaked from pathological tissues across the body, many of which are commonly obtainable through non-invasive procedures (1, 2). Driven by these factors, research interests have soared a few decades ago toward biomarker discovery by examining body fluid proteomes. It is highly plausible that empowered by innovative high-throughput technologies, modern proteomic studies have successfully identified a large number of proteins in various body fluids such as plasma, serum, saliva and urine (3).
With great effort by a few large consortiums, several community-based proteomic databases have been developed in the past decades. For example, in 2002, the international Human Proteome Organization initiated the Human Plasma Proteome Project and reported human plasma and serum protein constituents in its online databases (4). Another similar database, named Plasma Proteome Database, archived more than 10 000 proteins detected in human blood (5). Additionally, the Proteomics Identifications database (6) and Human Plasma PeptideAtlas (7) report a total of 3509 high-confidence plasma proteins. More recently, the extracellular vesicles community also reports new proteins identified in exosomes in multiple different resources including blood and breast milk, e.g. in ExoCarta (8). Additionally, the global Human Proteome Project (HPP) announces a set of mass spectrometry (MS) data interpretation guidelines that are presented to the broader research community (9).
Our team has recently conducted a systematical assessment of human proteome identified using quantitative proteomics tools such as MS and computational predictive models, as documented in a recent review article (10). To expand this effort, we developed a new human body fluid proteome (HBFP) database to organize 11 827 unique proteins reported in 164 scientific articles since 2001, which has a maximal false discovery rate (FDR) of 0.01 on both the peptide and protein levels. Until today, this database stores information about proteins from 17 types of body fluids including plasma/serum, saliva, urine, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), seminal fluid (SF), amniotic fluid, tear fluid, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), milk, synovial fluid, nipple aspirate fluid, cervical-vaginal fluid, pleural effusion, sputum, exhaled breath condensate, pancreatic juice and sweat. For each protein entry, description about protein secretion information, literature source, abundances, confidence and functional annotation is provided. This database system also provides users easy access to data visualization and download and functional analysis based on Gene Ontology (GO) and pathways.
Database content and design
Protein entries
We have manually collected proteins reported in 17 types of body fluids by carefully reviewing 164 scientific references published since 2001 based on a PubMed search with FDR ≤1% on both the peptide and protein levels.
In the HBFP database, each protein is assigned with a unique identifier of UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot accession (UniProt release 2020_06) (11). Since different identifiers have been mixed used in the referenced studies, we first used conversion tools at BioDBnet (https://biodbnet-abcc.ncifcrf.gov/) (12) and UniProt (https://www.UniProt.org/) to confidently convert different identifiers to UniProt accession numbers. The common identifiers involved in this study include International Protein Index ID [hosted at European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI) (closed in 2011)], GI number (from Genbank database), RefSeq protein accession (from RefSeq database), Gene name/symbol (from NCBI Gene database) and UniProt protein/entry name (from UniProt database). The ID conversion process is shown in Figure 1. During the conversion, poorly curated proteins with ambiguous identifiers were eliminated. For examples, many International Protein Index ID links to unclearly described instances that cannot be mapped to a UniProt entry are excluded.
Database utilities
The interface of the HBFP database is constructed by PHP, while the database system is based on MySQL. The main contents of the current database include query and browse pages described as follows.
Querying page
As one of the most important functions, the querying page allows users to search for body fluid proteins based on different types of input including protein ID, gene name, and protein or gene sequence. When given a FASTA input, BLASTp or BLASTn is used to translate sequence input to the best-match protein entry. The top hit (the highest bit score) from the BLAST search is considered the best match of the query. Figure 2 illustrates the workflow and content of querying page.
The annotation of each protein contains the following information:
Protein ID/name/entry name
Gene name
Associated body fluid type along with indicated discovery confidence (explained in the next section)
References and protein abundance information where the protein is reported
External links to public databases including UniProt, PeptideAtlas and NeXtProt (13), MassIVE (14)
Functional annotation based on the KEGG pathway (15) and GO (16)
Browsing page
This page provides an overview list of proteins associated with 17 types of body fluids and links to view and download selected proteins.
Database highlights
Data statistics
When determining the inclusion of reported proteins, we applied the following criteria for credibility of the MS evidence. First, for papers that issued peptide sequence details, we remapped all those peptide sequences to neXtProt (release 2021-02-15) using the neXtProt peptide uniqueness checker to remove unreliable matches (17). Specifically, we applied guideline #15 of HPP Guidelines 2.1 (9) to include proteins that contain at least two non-nested uniquely mapping peptides of nine amino acids into the HBFP database. According to this criterion, 7354 proteins were confirmed confidently. Another 4473 proteins were also included as they were not explicitly provided with peptide sequence information but have more than two unique peptides.
The overall statistics about the protein entries and references in terms of each body fluid are summarized in Table 1. The current HBFP database contains 11 827 distinct proteins from 17 types of body fluids. Note that urine exceeds all other body fluids in terms of protein counts while blood is at the second rank. All data are made publicly available in the HBFP and via links at https://bmbl.bmi.osumc.edu/HBFP/.
| . | Statistics . | . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body fluid types . | Number of protein entries . | Number of references . | References . | |
| 1 | Plasma/serum | 5790 | 38 | (18–55) |
| 2 | Saliva | 2758 | 21 | (19, 56–75) |
| 3 | Urine | 7330 | 23 | (19, 76–97) |
| 4 | CSF | 4364 | 12 | (19, 90, 98–107) |
| 5 | SF | 4084 | 5 | (108–112) |
| 6 | Amniotic fluid | 3025 | 6 | (19, 113–117) |
| 7 | Tear fluid (TF) | 1882 | 11 | (118–128) |
| 8 | BALF | 3434 | 6 | (41, 129–133) |
| 9 | Milk | 2457 | 14 | (134–147) |
| 10 | Synovial fluid | 1637 | 7 | (148–154) |
| 11 | Nipple aspirate fluid | 1734 | 5 | (155–159) |
| 12 | Cervical–vaginal fluid | 949 | 4 | (160–163) |
| 13 | Pleural effusion | 1519 | 3 | (164–166) |
| 14 | Sputum | 1809 | 3 | (167–169) |
| 15 | Exhaled breath condensate | 351 | 5 | (170–174) |
| 16 | Pancreatic juice | 702 | 4 | (175–178) |
| 17 | Sweat | 1244 | 3 | (179–181) |
| Total (non-redundant) | 11 827 | 164 | ||
| . | Statistics . | . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body fluid types . | Number of protein entries . | Number of references . | References . | |
| 1 | Plasma/serum | 5790 | 38 | (18–55) |
| 2 | Saliva | 2758 | 21 | (19, 56–75) |
| 3 | Urine | 7330 | 23 | (19, 76–97) |
| 4 | CSF | 4364 | 12 | (19, 90, 98–107) |
| 5 | SF | 4084 | 5 | (108–112) |
| 6 | Amniotic fluid | 3025 | 6 | (19, 113–117) |
| 7 | Tear fluid (TF) | 1882 | 11 | (118–128) |
| 8 | BALF | 3434 | 6 | (41, 129–133) |
| 9 | Milk | 2457 | 14 | (134–147) |
| 10 | Synovial fluid | 1637 | 7 | (148–154) |
| 11 | Nipple aspirate fluid | 1734 | 5 | (155–159) |
| 12 | Cervical–vaginal fluid | 949 | 4 | (160–163) |
| 13 | Pleural effusion | 1519 | 3 | (164–166) |
| 14 | Sputum | 1809 | 3 | (167–169) |
| 15 | Exhaled breath condensate | 351 | 5 | (170–174) |
| 16 | Pancreatic juice | 702 | 4 | (175–178) |
| 17 | Sweat | 1244 | 3 | (179–181) |
| Total (non-redundant) | 11 827 | 164 | ||
| . | Statistics . | . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body fluid types . | Number of protein entries . | Number of references . | References . | |
| 1 | Plasma/serum | 5790 | 38 | (18–55) |
| 2 | Saliva | 2758 | 21 | (19, 56–75) |
| 3 | Urine | 7330 | 23 | (19, 76–97) |
| 4 | CSF | 4364 | 12 | (19, 90, 98–107) |
| 5 | SF | 4084 | 5 | (108–112) |
| 6 | Amniotic fluid | 3025 | 6 | (19, 113–117) |
| 7 | Tear fluid (TF) | 1882 | 11 | (118–128) |
| 8 | BALF | 3434 | 6 | (41, 129–133) |
| 9 | Milk | 2457 | 14 | (134–147) |
| 10 | Synovial fluid | 1637 | 7 | (148–154) |
| 11 | Nipple aspirate fluid | 1734 | 5 | (155–159) |
| 12 | Cervical–vaginal fluid | 949 | 4 | (160–163) |
| 13 | Pleural effusion | 1519 | 3 | (164–166) |
| 14 | Sputum | 1809 | 3 | (167–169) |
| 15 | Exhaled breath condensate | 351 | 5 | (170–174) |
| 16 | Pancreatic juice | 702 | 4 | (175–178) |
| 17 | Sweat | 1244 | 3 | (179–181) |
| Total (non-redundant) | 11 827 | 164 | ||
| . | Statistics . | . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body fluid types . | Number of protein entries . | Number of references . | References . | |
| 1 | Plasma/serum | 5790 | 38 | (18–55) |
| 2 | Saliva | 2758 | 21 | (19, 56–75) |
| 3 | Urine | 7330 | 23 | (19, 76–97) |
| 4 | CSF | 4364 | 12 | (19, 90, 98–107) |
| 5 | SF | 4084 | 5 | (108–112) |
| 6 | Amniotic fluid | 3025 | 6 | (19, 113–117) |
| 7 | Tear fluid (TF) | 1882 | 11 | (118–128) |
| 8 | BALF | 3434 | 6 | (41, 129–133) |
| 9 | Milk | 2457 | 14 | (134–147) |
| 10 | Synovial fluid | 1637 | 7 | (148–154) |
| 11 | Nipple aspirate fluid | 1734 | 5 | (155–159) |
| 12 | Cervical–vaginal fluid | 949 | 4 | (160–163) |
| 13 | Pleural effusion | 1519 | 3 | (164–166) |
| 14 | Sputum | 1809 | 3 | (167–169) |
| 15 | Exhaled breath condensate | 351 | 5 | (170–174) |
| 16 | Pancreatic juice | 702 | 4 | (175–178) |
| 17 | Sweat | 1244 | 3 | (179–181) |
| Total (non-redundant) | 11 827 | 164 | ||
Protein abundance
In order to provide users experimental evidence from the original study, this database also displays relatively abundant information from the corresponding literature studies. General proteomics approaches using MS identify proteins by matching identified peptides against predefined protein sequence databases. The qualitative measures of protein reported in the original reference include the following: (i) peptide information: most of cited studies provide explicit information about peptide sequence, the total number of peptides, MS counts or the percent sequence coverage; (ii) differential expression information including fold change (positive value demonstrates up-regulated expression and negative value indicates down-regulated expression), up- or down-regulated expression in case vs. control or (normalized) spectral counts and (iii) other statistical information including FDR, relative standard deviation and the number of times across different samples or experiments, as shown in Figure 3.
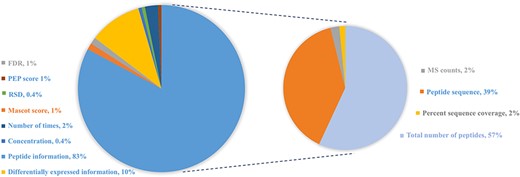
Distribution of protein abundance methods in HBFP database based on a number of original quantitative analysis methods from the original literature studies. Note that the sum of protein abundance is not 100% since not all of the literature studies provide quantitative analysis information.
Confidence score
For example, there are 38 literature studies related to blood in the HBFP, so |${N_i} = 38$|, |$FD{R_i} = 0.195$| and |${A_i} = 0.805$|. The protein O14791 is identified in blood by 19 independent studies, i.e. |${M_j} = 19$|. As a result, the calculated |${C_{i,j}}$| score for O14791 in blood is |$0.895$|. Meanwhile, protein Q9UJV9 only is identified in one paper for blood, so |${M_j} = 1$| and |${C_{i,j}} = {A_i} = 0.805$|. It means that protein Q9UJV9 maintains only the confidence level in the combined datasets of blood. Specifically, protein P01833 is identified in milk by 14 studies, and a total of 14 literature studies on milk are included in the HBFP, so protein P01833 maintains the original confidence level, i.e. 0.99. The larger the |$C$| score, the higher the confidence that a protein reported in that fluid will be. Note that this score can only be compared within the same type of body fluid.
Database applications
Data access
The website can be accessed through https://bmbl.bmi.osumc.edu/HBFP/.
Query
All proteins can be easily accessed by searching protein ID, gene name, protein sequence (FASTA) or gene sequence (FASTA) (<50 items per query) (Figure 4A and B as an example). A BLAST (182) is performed locally to find the best match when the sequence FASTA format is given. For each protein, detailed information is displayed (Figure 4C). Users can connect directly to the PubMed or Google Scholar to view the original study through the provided links. Four databases (UniProt, PeptideAtlas, NeXtProt and MassIVE) are cross-linked for additional protein annotation, while the KEGG pathway and GO are focused on the functional aspects (Figure 4D).
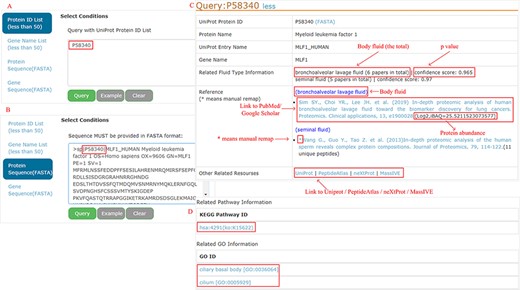
Example of query response with input as ‘P58340’ in the protein ID and protein sequence box.
Download
HBFP allows users to browse the entire protein list in each body fluid, where the proteins are ordered based on descending confidence scores. Users can check and download all entries of the selected body fluid type in one go, as shown in Figure 5.
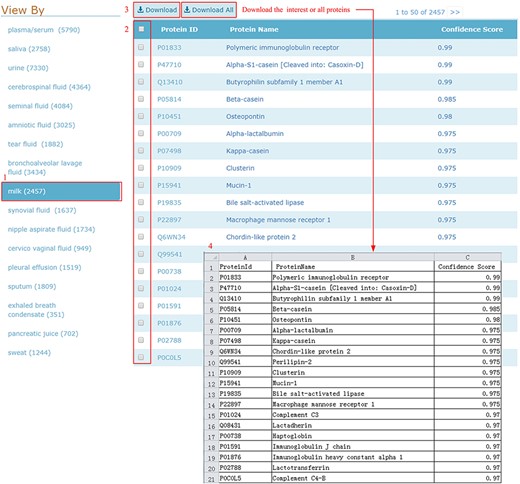
Download illustration where user can choose the body fluid name and download the proteins of interest or all proteins.
Demo of comparative analysis using the HBFP database
Body fluid analysis
Many proteins in the HBFP database have a broad distribution in terms of body fluid types. An internal comparative analysis across different fluids can provide further information regarding the specificity of a proposed marker protein. Of 11 827 identified proteins, 66.8% are identified in at least two body fluids (Figure 6). A total of 93 proteins (0.79%) are shared among all analyzed body fluids, which may indicate that these proteins are essential for various life activities (Table 2).
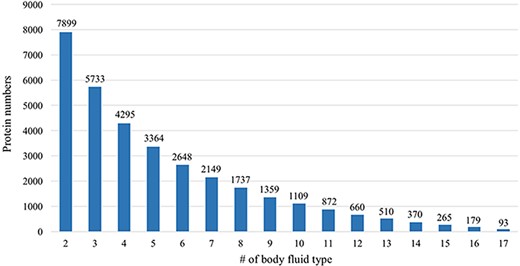
Comparative analysis across different body fluids. Seven thousand eight hundred and ninety-nine (7899) proteins are presented in at least two body fluids and 5733 proteins existed in at least three body fluids. Only 93 proteins exist in all 17 body fluids.
| . | UniProt accession number . | Protein name . | Gene name . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | P11021 | Endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP | HSPA5 |
| 2 | P55072 | Transitional endoplasmic reticulum ATPase | VCP |
| 3 | P13647 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 5 | KRT5 |
| 4 | O00299 | Chloride intracellular channel protein 1 | CLIC1 |
| 5 | P02787 | Serotransferrin | TF |
| 6 | P22314 | Ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme 1 | UBA1 |
| 7 | P13645 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 10 | KRT10 |
| 8 | P02533 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 14 | KRT14 |
| 9 | P07237 | Protein disulfide-isomerase | P4HB |
| 10 | P06576 | ATP synthase subunit beta, mitochondrial | ATP5F1B |
| 11 | P30041 | Peroxiredoxin-6 | PRDX6 |
| 12 | P63104 | 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta | YWHAZ |
| 13 | P62258 | 14-3-3 protein epsilon | YWHAE |
| 14 | P14923 | Junction plakoglobin | JUP |
| 15 | P04040 | Catalase | CAT |
| 16 | P01834 | Immunoglobulin kappa constant | IGKC |
| 17 | P06702 | Protein S100-A9 | S100A9 |
| 18 | P52209 | 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, decarboxylating | PGD |
| 19 | P18669 | Phosphoglycerate mutase 1 | PGAM1 |
| 20 | P14618 | Pyruvate kinase PKM | PKM |
| 21 | P61981 | 14-3-3 protein gamma | YWHAG |
| 22 | P07384 | Calpain-1 catalytic subunit | CAPN1 |
| 23 | P50395 | Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor beta | GDI2 |
| 24 | Q00610 | Clathrin heavy chain 1 | CLTC |
| 25 | P26641 | Elongation factor 1-gamma | EEF1G |
| 26 | P32119 | Peroxiredoxin-2 | PRDX2 |
| 27 | P19971 | Thymidine phosphorylase | TYMP |
| 28 | P26038 | Moesin | MSN |
| 29 | P40121 | Macrophage-capping protein | CAPG |
| 30 | P35754 | Glutaredoxin-1 | GLRX |
| 31 | P01009 | Alpha-1-antitrypsin | SERPINA1 |
| 32 | P01860 | Immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 3 | IGHG3 |
| 33 | P06753 | Tropomyosin alpha-3 chain | TPM3 |
| 34 | P68871 | Hemoglobin subunit beta | HBB |
| 35 | P62805 | Histone H4 | H4C1 |
| 36 | P30086 | Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 1 | PEBP1 |
| 37 | P35579 | Myosin-9 | MYH9 |
| 38 | P01023 | Alpha-2-macroglobulin | A2M |
| 39 | Q06830 | Peroxiredoxin-1 | PRDX1 |
| 40 | P02042 | Hemoglobin subunit delta | HBD |
| 41 | P07737 | Profilin-1 | PFN1 |
| 42 | P80188 | Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin | LCN2 |
| 43 | P02679 | Fibrinogen gamma chain | FGG |
| 44 | P40925 | Malate dehydrogenase, cytoplasmic | MDH1 |
| 45 | P08758 | Annexin A5 | ANXA5 |
| 46 | P46940 | Ras GTPase-activating-like protein IQGAP1 | IQGAP1 |
| 47 | P01833 | Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor | PIGR |
| 48 | P31949 | Protein S100-A11 | S100A11 |
| 49 | P04792 | Heat shock protein beta-1 | HSPB1 |
| 50 | P07339 | Cathepsin D | CTSD |
| 51 | P01857 | Immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 1 | IGHG1 |
| 52 | P06733 | Alpha-enolase | ENO1 |
| 53 | P23284 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase B | PPIB |
| 54 | P02647 | Apolipoprotein A-I | APOA1 |
| 55 | O43707 | Alpha-actinin-4 | ACTN4 |
| 56 | P30740 | Leukocyte elastase inhibitor | SERPINB1 |
| 57 | Q16610 | Extracellular matrix protein 1 | ECM1 |
| 58 | P60709 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | ACTB |
| 59 | P15924 | Desmoplakin | DSP |
| 60 | P62937 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A | PPIA |
| 61 | P17931 | Galectin-3 | LGALS3 |
| 62 | P00491 | Purine nucleoside phosphorylase | PNP |
| 63 | P04080 | Cystatin-B | CSTB |
| 64 | P02788 | Lactotransferrin | LTF |
| 65 | P13639 | Elongation factor 2 | EEF2 |
| 66 | P35527 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 9 | KRT9 |
| 67 | P06396 | Gelsolin | GSN |
| 68 | P59998 | Actin-related protein 2/3 complex subunit 4 | ARPC4 |
| 69 | P25311 | Zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein | AZGP1 |
| 70 | P02768 | Albumin | ALB |
| 71 | P61160 | Actin-related protein 2 | ACTR2 |
| 72 | P04406 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | GAPDH |
| 73 | P60174 | Triosephosphate isomerase | TPI1 |
| 74 | P18206 | Vinculin | VCL |
| 75 | P08670 | Vimentin | VIM |
| 76 | P10599 | Thioredoxin | TXN |
| 77 | P11142 | Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein | HSPA8 |
| 78 | P01011 | Alpha-1-antichymotrypsin | SERPINA3 |
| 79 | P04075 | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase A | ALDOA |
| 80 | P04264 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1 | KRT1 |
| 81 | P37837 | Transaldolase | TALDO1 |
| 82 | P35908 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 2 epidermal | KRT2 |
| 83 | P02545 | Prelamin-A/C | LMNA |
| 84 | P69905 | Hemoglobin subunit alpha | HBA1 |
| 85 | P07900 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha | HSP90AA1 |
| 86 | P29401 | Transketolase | TKT |
| 87 | P00558 | Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 | PGK1 |
| 88 | P00338 | L-lactate dehydrogenase A chain | LDHA |
| 89 | P01861 | Immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 4 | IGHG4 |
| 90 | P05109 | Protein S100-A8 | S100A8 |
| 91 | P04083 | Annexin A1 | ANXA1 |
| 92 | P01024 | Complement C3 | C3 |
| 93 | P09211 | Glutathione S-transferase P | GSTP1 |
| . | UniProt accession number . | Protein name . | Gene name . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | P11021 | Endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP | HSPA5 |
| 2 | P55072 | Transitional endoplasmic reticulum ATPase | VCP |
| 3 | P13647 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 5 | KRT5 |
| 4 | O00299 | Chloride intracellular channel protein 1 | CLIC1 |
| 5 | P02787 | Serotransferrin | TF |
| 6 | P22314 | Ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme 1 | UBA1 |
| 7 | P13645 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 10 | KRT10 |
| 8 | P02533 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 14 | KRT14 |
| 9 | P07237 | Protein disulfide-isomerase | P4HB |
| 10 | P06576 | ATP synthase subunit beta, mitochondrial | ATP5F1B |
| 11 | P30041 | Peroxiredoxin-6 | PRDX6 |
| 12 | P63104 | 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta | YWHAZ |
| 13 | P62258 | 14-3-3 protein epsilon | YWHAE |
| 14 | P14923 | Junction plakoglobin | JUP |
| 15 | P04040 | Catalase | CAT |
| 16 | P01834 | Immunoglobulin kappa constant | IGKC |
| 17 | P06702 | Protein S100-A9 | S100A9 |
| 18 | P52209 | 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, decarboxylating | PGD |
| 19 | P18669 | Phosphoglycerate mutase 1 | PGAM1 |
| 20 | P14618 | Pyruvate kinase PKM | PKM |
| 21 | P61981 | 14-3-3 protein gamma | YWHAG |
| 22 | P07384 | Calpain-1 catalytic subunit | CAPN1 |
| 23 | P50395 | Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor beta | GDI2 |
| 24 | Q00610 | Clathrin heavy chain 1 | CLTC |
| 25 | P26641 | Elongation factor 1-gamma | EEF1G |
| 26 | P32119 | Peroxiredoxin-2 | PRDX2 |
| 27 | P19971 | Thymidine phosphorylase | TYMP |
| 28 | P26038 | Moesin | MSN |
| 29 | P40121 | Macrophage-capping protein | CAPG |
| 30 | P35754 | Glutaredoxin-1 | GLRX |
| 31 | P01009 | Alpha-1-antitrypsin | SERPINA1 |
| 32 | P01860 | Immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 3 | IGHG3 |
| 33 | P06753 | Tropomyosin alpha-3 chain | TPM3 |
| 34 | P68871 | Hemoglobin subunit beta | HBB |
| 35 | P62805 | Histone H4 | H4C1 |
| 36 | P30086 | Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 1 | PEBP1 |
| 37 | P35579 | Myosin-9 | MYH9 |
| 38 | P01023 | Alpha-2-macroglobulin | A2M |
| 39 | Q06830 | Peroxiredoxin-1 | PRDX1 |
| 40 | P02042 | Hemoglobin subunit delta | HBD |
| 41 | P07737 | Profilin-1 | PFN1 |
| 42 | P80188 | Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin | LCN2 |
| 43 | P02679 | Fibrinogen gamma chain | FGG |
| 44 | P40925 | Malate dehydrogenase, cytoplasmic | MDH1 |
| 45 | P08758 | Annexin A5 | ANXA5 |
| 46 | P46940 | Ras GTPase-activating-like protein IQGAP1 | IQGAP1 |
| 47 | P01833 | Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor | PIGR |
| 48 | P31949 | Protein S100-A11 | S100A11 |
| 49 | P04792 | Heat shock protein beta-1 | HSPB1 |
| 50 | P07339 | Cathepsin D | CTSD |
| 51 | P01857 | Immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 1 | IGHG1 |
| 52 | P06733 | Alpha-enolase | ENO1 |
| 53 | P23284 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase B | PPIB |
| 54 | P02647 | Apolipoprotein A-I | APOA1 |
| 55 | O43707 | Alpha-actinin-4 | ACTN4 |
| 56 | P30740 | Leukocyte elastase inhibitor | SERPINB1 |
| 57 | Q16610 | Extracellular matrix protein 1 | ECM1 |
| 58 | P60709 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | ACTB |
| 59 | P15924 | Desmoplakin | DSP |
| 60 | P62937 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A | PPIA |
| 61 | P17931 | Galectin-3 | LGALS3 |
| 62 | P00491 | Purine nucleoside phosphorylase | PNP |
| 63 | P04080 | Cystatin-B | CSTB |
| 64 | P02788 | Lactotransferrin | LTF |
| 65 | P13639 | Elongation factor 2 | EEF2 |
| 66 | P35527 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 9 | KRT9 |
| 67 | P06396 | Gelsolin | GSN |
| 68 | P59998 | Actin-related protein 2/3 complex subunit 4 | ARPC4 |
| 69 | P25311 | Zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein | AZGP1 |
| 70 | P02768 | Albumin | ALB |
| 71 | P61160 | Actin-related protein 2 | ACTR2 |
| 72 | P04406 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | GAPDH |
| 73 | P60174 | Triosephosphate isomerase | TPI1 |
| 74 | P18206 | Vinculin | VCL |
| 75 | P08670 | Vimentin | VIM |
| 76 | P10599 | Thioredoxin | TXN |
| 77 | P11142 | Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein | HSPA8 |
| 78 | P01011 | Alpha-1-antichymotrypsin | SERPINA3 |
| 79 | P04075 | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase A | ALDOA |
| 80 | P04264 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1 | KRT1 |
| 81 | P37837 | Transaldolase | TALDO1 |
| 82 | P35908 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 2 epidermal | KRT2 |
| 83 | P02545 | Prelamin-A/C | LMNA |
| 84 | P69905 | Hemoglobin subunit alpha | HBA1 |
| 85 | P07900 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha | HSP90AA1 |
| 86 | P29401 | Transketolase | TKT |
| 87 | P00558 | Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 | PGK1 |
| 88 | P00338 | L-lactate dehydrogenase A chain | LDHA |
| 89 | P01861 | Immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 4 | IGHG4 |
| 90 | P05109 | Protein S100-A8 | S100A8 |
| 91 | P04083 | Annexin A1 | ANXA1 |
| 92 | P01024 | Complement C3 | C3 |
| 93 | P09211 | Glutathione S-transferase P | GSTP1 |
| . | UniProt accession number . | Protein name . | Gene name . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | P11021 | Endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP | HSPA5 |
| 2 | P55072 | Transitional endoplasmic reticulum ATPase | VCP |
| 3 | P13647 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 5 | KRT5 |
| 4 | O00299 | Chloride intracellular channel protein 1 | CLIC1 |
| 5 | P02787 | Serotransferrin | TF |
| 6 | P22314 | Ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme 1 | UBA1 |
| 7 | P13645 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 10 | KRT10 |
| 8 | P02533 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 14 | KRT14 |
| 9 | P07237 | Protein disulfide-isomerase | P4HB |
| 10 | P06576 | ATP synthase subunit beta, mitochondrial | ATP5F1B |
| 11 | P30041 | Peroxiredoxin-6 | PRDX6 |
| 12 | P63104 | 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta | YWHAZ |
| 13 | P62258 | 14-3-3 protein epsilon | YWHAE |
| 14 | P14923 | Junction plakoglobin | JUP |
| 15 | P04040 | Catalase | CAT |
| 16 | P01834 | Immunoglobulin kappa constant | IGKC |
| 17 | P06702 | Protein S100-A9 | S100A9 |
| 18 | P52209 | 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, decarboxylating | PGD |
| 19 | P18669 | Phosphoglycerate mutase 1 | PGAM1 |
| 20 | P14618 | Pyruvate kinase PKM | PKM |
| 21 | P61981 | 14-3-3 protein gamma | YWHAG |
| 22 | P07384 | Calpain-1 catalytic subunit | CAPN1 |
| 23 | P50395 | Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor beta | GDI2 |
| 24 | Q00610 | Clathrin heavy chain 1 | CLTC |
| 25 | P26641 | Elongation factor 1-gamma | EEF1G |
| 26 | P32119 | Peroxiredoxin-2 | PRDX2 |
| 27 | P19971 | Thymidine phosphorylase | TYMP |
| 28 | P26038 | Moesin | MSN |
| 29 | P40121 | Macrophage-capping protein | CAPG |
| 30 | P35754 | Glutaredoxin-1 | GLRX |
| 31 | P01009 | Alpha-1-antitrypsin | SERPINA1 |
| 32 | P01860 | Immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 3 | IGHG3 |
| 33 | P06753 | Tropomyosin alpha-3 chain | TPM3 |
| 34 | P68871 | Hemoglobin subunit beta | HBB |
| 35 | P62805 | Histone H4 | H4C1 |
| 36 | P30086 | Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 1 | PEBP1 |
| 37 | P35579 | Myosin-9 | MYH9 |
| 38 | P01023 | Alpha-2-macroglobulin | A2M |
| 39 | Q06830 | Peroxiredoxin-1 | PRDX1 |
| 40 | P02042 | Hemoglobin subunit delta | HBD |
| 41 | P07737 | Profilin-1 | PFN1 |
| 42 | P80188 | Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin | LCN2 |
| 43 | P02679 | Fibrinogen gamma chain | FGG |
| 44 | P40925 | Malate dehydrogenase, cytoplasmic | MDH1 |
| 45 | P08758 | Annexin A5 | ANXA5 |
| 46 | P46940 | Ras GTPase-activating-like protein IQGAP1 | IQGAP1 |
| 47 | P01833 | Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor | PIGR |
| 48 | P31949 | Protein S100-A11 | S100A11 |
| 49 | P04792 | Heat shock protein beta-1 | HSPB1 |
| 50 | P07339 | Cathepsin D | CTSD |
| 51 | P01857 | Immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 1 | IGHG1 |
| 52 | P06733 | Alpha-enolase | ENO1 |
| 53 | P23284 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase B | PPIB |
| 54 | P02647 | Apolipoprotein A-I | APOA1 |
| 55 | O43707 | Alpha-actinin-4 | ACTN4 |
| 56 | P30740 | Leukocyte elastase inhibitor | SERPINB1 |
| 57 | Q16610 | Extracellular matrix protein 1 | ECM1 |
| 58 | P60709 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | ACTB |
| 59 | P15924 | Desmoplakin | DSP |
| 60 | P62937 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A | PPIA |
| 61 | P17931 | Galectin-3 | LGALS3 |
| 62 | P00491 | Purine nucleoside phosphorylase | PNP |
| 63 | P04080 | Cystatin-B | CSTB |
| 64 | P02788 | Lactotransferrin | LTF |
| 65 | P13639 | Elongation factor 2 | EEF2 |
| 66 | P35527 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 9 | KRT9 |
| 67 | P06396 | Gelsolin | GSN |
| 68 | P59998 | Actin-related protein 2/3 complex subunit 4 | ARPC4 |
| 69 | P25311 | Zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein | AZGP1 |
| 70 | P02768 | Albumin | ALB |
| 71 | P61160 | Actin-related protein 2 | ACTR2 |
| 72 | P04406 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | GAPDH |
| 73 | P60174 | Triosephosphate isomerase | TPI1 |
| 74 | P18206 | Vinculin | VCL |
| 75 | P08670 | Vimentin | VIM |
| 76 | P10599 | Thioredoxin | TXN |
| 77 | P11142 | Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein | HSPA8 |
| 78 | P01011 | Alpha-1-antichymotrypsin | SERPINA3 |
| 79 | P04075 | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase A | ALDOA |
| 80 | P04264 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1 | KRT1 |
| 81 | P37837 | Transaldolase | TALDO1 |
| 82 | P35908 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 2 epidermal | KRT2 |
| 83 | P02545 | Prelamin-A/C | LMNA |
| 84 | P69905 | Hemoglobin subunit alpha | HBA1 |
| 85 | P07900 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha | HSP90AA1 |
| 86 | P29401 | Transketolase | TKT |
| 87 | P00558 | Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 | PGK1 |
| 88 | P00338 | L-lactate dehydrogenase A chain | LDHA |
| 89 | P01861 | Immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 4 | IGHG4 |
| 90 | P05109 | Protein S100-A8 | S100A8 |
| 91 | P04083 | Annexin A1 | ANXA1 |
| 92 | P01024 | Complement C3 | C3 |
| 93 | P09211 | Glutathione S-transferase P | GSTP1 |
| . | UniProt accession number . | Protein name . | Gene name . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | P11021 | Endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP | HSPA5 |
| 2 | P55072 | Transitional endoplasmic reticulum ATPase | VCP |
| 3 | P13647 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 5 | KRT5 |
| 4 | O00299 | Chloride intracellular channel protein 1 | CLIC1 |
| 5 | P02787 | Serotransferrin | TF |
| 6 | P22314 | Ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme 1 | UBA1 |
| 7 | P13645 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 10 | KRT10 |
| 8 | P02533 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 14 | KRT14 |
| 9 | P07237 | Protein disulfide-isomerase | P4HB |
| 10 | P06576 | ATP synthase subunit beta, mitochondrial | ATP5F1B |
| 11 | P30041 | Peroxiredoxin-6 | PRDX6 |
| 12 | P63104 | 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta | YWHAZ |
| 13 | P62258 | 14-3-3 protein epsilon | YWHAE |
| 14 | P14923 | Junction plakoglobin | JUP |
| 15 | P04040 | Catalase | CAT |
| 16 | P01834 | Immunoglobulin kappa constant | IGKC |
| 17 | P06702 | Protein S100-A9 | S100A9 |
| 18 | P52209 | 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, decarboxylating | PGD |
| 19 | P18669 | Phosphoglycerate mutase 1 | PGAM1 |
| 20 | P14618 | Pyruvate kinase PKM | PKM |
| 21 | P61981 | 14-3-3 protein gamma | YWHAG |
| 22 | P07384 | Calpain-1 catalytic subunit | CAPN1 |
| 23 | P50395 | Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor beta | GDI2 |
| 24 | Q00610 | Clathrin heavy chain 1 | CLTC |
| 25 | P26641 | Elongation factor 1-gamma | EEF1G |
| 26 | P32119 | Peroxiredoxin-2 | PRDX2 |
| 27 | P19971 | Thymidine phosphorylase | TYMP |
| 28 | P26038 | Moesin | MSN |
| 29 | P40121 | Macrophage-capping protein | CAPG |
| 30 | P35754 | Glutaredoxin-1 | GLRX |
| 31 | P01009 | Alpha-1-antitrypsin | SERPINA1 |
| 32 | P01860 | Immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 3 | IGHG3 |
| 33 | P06753 | Tropomyosin alpha-3 chain | TPM3 |
| 34 | P68871 | Hemoglobin subunit beta | HBB |
| 35 | P62805 | Histone H4 | H4C1 |
| 36 | P30086 | Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 1 | PEBP1 |
| 37 | P35579 | Myosin-9 | MYH9 |
| 38 | P01023 | Alpha-2-macroglobulin | A2M |
| 39 | Q06830 | Peroxiredoxin-1 | PRDX1 |
| 40 | P02042 | Hemoglobin subunit delta | HBD |
| 41 | P07737 | Profilin-1 | PFN1 |
| 42 | P80188 | Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin | LCN2 |
| 43 | P02679 | Fibrinogen gamma chain | FGG |
| 44 | P40925 | Malate dehydrogenase, cytoplasmic | MDH1 |
| 45 | P08758 | Annexin A5 | ANXA5 |
| 46 | P46940 | Ras GTPase-activating-like protein IQGAP1 | IQGAP1 |
| 47 | P01833 | Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor | PIGR |
| 48 | P31949 | Protein S100-A11 | S100A11 |
| 49 | P04792 | Heat shock protein beta-1 | HSPB1 |
| 50 | P07339 | Cathepsin D | CTSD |
| 51 | P01857 | Immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 1 | IGHG1 |
| 52 | P06733 | Alpha-enolase | ENO1 |
| 53 | P23284 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase B | PPIB |
| 54 | P02647 | Apolipoprotein A-I | APOA1 |
| 55 | O43707 | Alpha-actinin-4 | ACTN4 |
| 56 | P30740 | Leukocyte elastase inhibitor | SERPINB1 |
| 57 | Q16610 | Extracellular matrix protein 1 | ECM1 |
| 58 | P60709 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | ACTB |
| 59 | P15924 | Desmoplakin | DSP |
| 60 | P62937 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A | PPIA |
| 61 | P17931 | Galectin-3 | LGALS3 |
| 62 | P00491 | Purine nucleoside phosphorylase | PNP |
| 63 | P04080 | Cystatin-B | CSTB |
| 64 | P02788 | Lactotransferrin | LTF |
| 65 | P13639 | Elongation factor 2 | EEF2 |
| 66 | P35527 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 9 | KRT9 |
| 67 | P06396 | Gelsolin | GSN |
| 68 | P59998 | Actin-related protein 2/3 complex subunit 4 | ARPC4 |
| 69 | P25311 | Zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein | AZGP1 |
| 70 | P02768 | Albumin | ALB |
| 71 | P61160 | Actin-related protein 2 | ACTR2 |
| 72 | P04406 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | GAPDH |
| 73 | P60174 | Triosephosphate isomerase | TPI1 |
| 74 | P18206 | Vinculin | VCL |
| 75 | P08670 | Vimentin | VIM |
| 76 | P10599 | Thioredoxin | TXN |
| 77 | P11142 | Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein | HSPA8 |
| 78 | P01011 | Alpha-1-antichymotrypsin | SERPINA3 |
| 79 | P04075 | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase A | ALDOA |
| 80 | P04264 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1 | KRT1 |
| 81 | P37837 | Transaldolase | TALDO1 |
| 82 | P35908 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 2 epidermal | KRT2 |
| 83 | P02545 | Prelamin-A/C | LMNA |
| 84 | P69905 | Hemoglobin subunit alpha | HBA1 |
| 85 | P07900 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha | HSP90AA1 |
| 86 | P29401 | Transketolase | TKT |
| 87 | P00558 | Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 | PGK1 |
| 88 | P00338 | L-lactate dehydrogenase A chain | LDHA |
| 89 | P01861 | Immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 4 | IGHG4 |
| 90 | P05109 | Protein S100-A8 | S100A8 |
| 91 | P04083 | Annexin A1 | ANXA1 |
| 92 | P01024 | Complement C3 | C3 |
| 93 | P09211 | Glutathione S-transferase P | GSTP1 |
Venn diagram and GO annotation
To take a closer look at this comparison, we focused on five body fluids that have the most protein counts, including blood, urine, CSF, SF) and BALF. An interesting discovery is that urine shares large numbers of common proteins with other fluids (Figure 7). A total of 4109, 3212, 2990 and 2950 proteins overlapped between the plasma and the other four body fluids (blood, CSF, SF and BALF, respectively). There are 965 proteins commonly detected in all five body fluids. The functional analysis using the BiNGO tool (183) in Cytoscape (184), reflecting information about cellular localization, molecular function and biological process of these proteins (Figure 8).

Venn diagram showing the common proteins among five body fluids (blood, urine, CSF, SF and BALF) that have the most number of proteins in the HBFP.
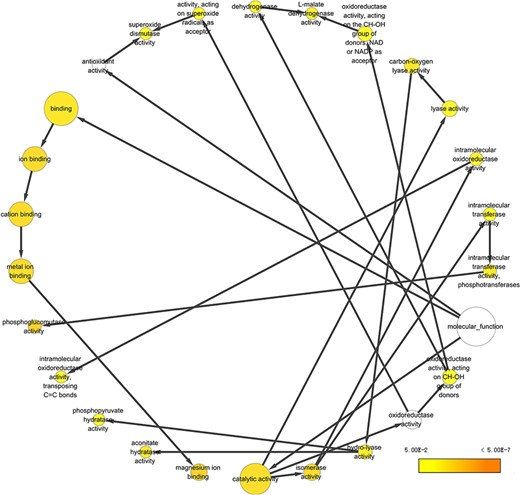
Example of GO annotation based on the 965 proteins common in five body fluids.
Conclusions
The new HBFP database developed in this study represents the first of its kind as a comprehensive reference resource of HBFP. All data are available through an open-access user-friendly Web platform. All protein entries were manually curated, which can be easily traced back to the original literature. Users can query and download proteins of interest to verify discovery in their own study or conduct an in silico analysis on human secretomes. We currently schedule a regular update every 6 months. The future plan is to include computationally identified proteins using statistical and machine learning approaches (185–191). In the past decade, many computational studies have revealed unique strengths in overcoming challenges in profiling-based proteomics research in terms of discovering new protein bioavailability and functions. Those computationally predicted proteins can serve as a secondary resource for biomarker discovery. In summary, by providing a wealth of information and functional analysis, we believe the HBFP database can be an excellent tool for the research community to explore human proteome in various body fluids.
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 62072212); Development Project of Jilin Province of China (nos 20200401083GX, 2020LY500L06 and 2020C003); Guangdong Key Project for Applied Fundamental Research (grant 2018KZDXM076); Jilin Province Key Laboratory of Big Data Intelligent Computing (no. 20180622002JC).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.



